
Mass Formation Psychology Meaning
Updated Oct 3, 2023
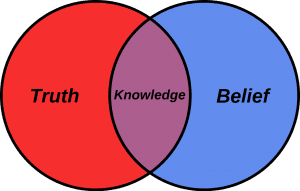
Before we get to the topic, let’s examine the meaning of mass formation psychology.
Mass formation psychology studies examine how collective ideologies and group dynamics can shape individual behaviour and beliefs. While much of the research in this field has focused on the formation and maintenance of fascist regimes, the concept of mass formation psychology has broader implications for understanding how group dynamics influence people in various contexts.
However, it is essential to approach this topic with a critical eye. Some scholars have questioned the assumptions that underpin the study of mass formation psychology, including the idea that individuals within a group are automatically susceptible to conformity or that groupthink is inherently negative. By adopting a contrarian perspective, we can interrogate the assumptions and beliefs that underpin the study of mass formation psychology and develop a more nuanced and critical understanding of the factors that underlie collective behaviour.
Understanding Mass Formation Psychology in Fascism
Mass formation psychology in the context of fascism is indeed a complex and controversial subject. While various scholars and thinkers have contributed to the understanding of this phenomenon, it is crucial to approach this topic with critical analysis and an awareness of the historical context in which these ideas were formulated.
Friedrich Nietzsche, an influential philosopher whose works spanned various topics, including morality, power, and the nature of human existence, has been examined concerning fascist ideologies. Nietzsche’s ideas on the will to power, the pursuit of greatness, and the rejection of egalitarianism have been selectively interpreted and appropriated by some fascist movements. However, it is crucial to note that Nietzsche’s philosophy is multifaceted and cannot be simplistically reduced to an endorsement of fascism.
Giovanni Gentile, an Italian philosopher closely associated with the ideology of Italian fascism, contributed to the development of fascist political theory. Gentile’s notion of the “ethical state” emphasized the collective over the individual and advocated for the subordination of personal interests to the national community. While Gentile’s ideas shaped the intellectual underpinnings of Italian fascism, it is important to recognize that his philosophy is specific to that historical context and should be understood within its historical limitations.
Niccolò Machiavelli, an influential political thinker from the Renaissance period, is often referenced in discussions of power and governance about fascism. Machiavelli’s pragmatic approach to politics, as outlined in his work “The Prince,” which emphasizes the acquisition and maintenance of power, has been selectively interpreted and utilized by various political movements, including fascist regimes. However, it is essential to consider the broader scope of Machiavelli’s political thought and not reduce it solely to its application in fascist contexts.
It is crucial to approach the study of mass formation psychology in fascism with intellectual rigour, recognizing that the interpretation and application of philosophical ideas within specific historical and political contexts can be complex and multifaceted. Understanding the contributions of Nietzsche, Gentile, Machiavelli, and other scholars requires examining their works in their entirety, considering the broader intellectual landscape, and critically assessing how their ideas have been appropriated and distorted by fascist ideologies.
The Will to Power: Nietzsche’s Influence on Fascist Thought
Nietzsche’s concept of the “will to power” indeed holds significance in understanding his influence on fascist thought. However, it is essential to approach this relationship with critical analysis and acknowledge the complexities and potential misinterpretations that may arise.
Nietzsche’s notion of the “will to power” refers to a fundamental drive within human beings to assert their strength and exercise dominance. This concept has been selectively appropriated by some fascist movements to justify the pursuit of power and the subjugation of others. The fascist interpretation of the “will to power” often emphasizes the superiority of certain individuals or groups over others, leading to the justification of oppression, violence, and the suppression of individual liberties.
However, it is crucial to recognize that Nietzsche’s philosophy is multifaceted and cannot be reduced solely to an endorsement of fascism or the justification of oppressive actions. Nietzsche’s writings explore a wide range of themes, including the critique of traditional morality, the exploration of the individual’s potential for self-overcoming, and the examination of the complexities of human existence. His philosophy is often open to multiple interpretations and has influenced thinkers across various ideological spectrums.
Moreover, it is essential to note that Nietzsche himself did not align with any political ideology, including fascism. He expressed strong criticisms of nationalism and the dangers of blind conformity to collective movements. Nietzsche’s ideas were often aimed at challenging conventional thinking and encouraging individuals to embrace their individuality and exercise their critical faculties.
While Nietzsche’s concept of the “will to power” has undoubtedly influenced fascist thought, it is crucial to approach his philosophy with nuance and recognize that it is subject to various interpretations. Understanding Nietzsche’s ideas in their broader context and critically analyzing how fascist ideologies have appropriated them is essential to grasp the complexities of his influence on fascist thought.
.
Critiquing the Will to Power: A Contrarian Perspective on Nietzsche
The contrarian perspective on Nietzsche’s notion of the “will to power” raises valid concerns regarding its potential interpretation as a justification for oppression and violence. It emphasizes the importance of shifting the focus from the domination of the strong over the weak to empowering individuals and building a society that upholds individual rights and freedoms.
Critics argue that an exclusive emphasis on the “will to power” can lead to a hierarchical worldview that justifies the subjugation of those deemed weaker or less powerful. This interpretation can be used to rationalize oppressive systems and marginalize certain individuals or groups based on arbitrary notions of strength or superiority.
In contrast, a contrarian viewpoint encourages a broader understanding of power that goes beyond domination and control. It highlights the importance of recognizing and valuing the inherent dignity and autonomy of every individual. Instead of perpetuating a power dynamic based on strength alone, this perspective emphasizes the need for a society that fosters equal opportunities, inclusivity, and the protection of individual rights.
Critics argue that focusing on empowering individuals and establishing a society that respects individual rights and freedoms is essential for creating a more just and equitable world. This approach values empathy, cooperation, and mutual respect rather than solely prioritizing the pursuit of power and dominance.
By challenging the potential pitfalls of an interpretation that justifies oppression and violence, the contrarian perspective encourages a more nuanced approach to Nietzsche’s ideas. It calls for critical analysis and a reevaluation of how power is understood and wielded in society, seeking to create a framework that promotes individual empowerment, social cohesion, and the protection of human rights.
The Primacy of the State: Gentile’s Vision for Fascist Society
Giovanni Gentile, an Italian philosopher closely associated with the ideology of Italian fascism, indeed emphasized the importance of the state in his vision of a fascist society. Gentile believed that the individual should submit to the will of the state, considering it the highest expression of the collective will. This concept aligns with the fascist ideology’s emphasis on the subordination of personal interests to the interests of the nation or state.
Gentile’s philosophy of the “ethical state” emphasized the role of the state in shaping and guiding the lives of its citizens. He argued that the state should be the ultimate authority, guiding individuals toward a higher collective purpose and ensuring the well-being of society as a whole. From Gentile’s perspective, the subordination of the individual to the state was necessary for achieving unity, order, and the realization of a shared national destiny.
On the other hand, Niccolò Machiavelli, a political thinker from the Renaissance period, is known for his pragmatic approach to politics. Machiavelli argued that successful leadership required using any means necessary to maintain power and achieve political goals. His influential work, “The Prince,” explores strategies for gaining and maintaining political control, including the use of deception, force, and manipulation.
While Gentile and Machiavelli share a focus on power and leadership, their perspectives differ in significant ways. Gentile’s emphasis on the primacy of the state and the subordination of the individual aligns with the collectivist ideology of fascism. In contrast, Machiavelli’s focus on political pragmatism primarily aims to provide advice to rulers on how to maintain power and navigate political realities.
It is important to approach the ideas of Gentile and Machiavelli critically, considering the historical context in which they developed their theories. While their ideas have influenced political thought, it is crucial to recognize that their perspectives are not universally accepted or uncontested. The primacy of the state advocated by Gentile and the pragmatic approach to leadership described by Machiavelli have been subject to criticism and debate throughout history.
Challenging Authoritarianism: A Contrarian View of Gentile’s Ideas
The contrarian perspective challenges Gentile’s notion of the importance of the state by highlighting concerns about authoritarianism and the potential suppression of individual freedoms. It argues that prioritizing individual liberty and autonomy is crucial for fostering a just and inclusive society where individuals can actively participate and contribute.
Critics of Gentile’s philosophy argue that placing the state above the individual can lead to the concentration of power in the hands of a few, resulting in the potential abuse of authority and the curtailment of individual rights. They emphasize the importance of protecting individual liberties, such as freedom of speech, assembly, and expression, as well as the right to dissent and question governmental actions.
Contrary to Gentile’s vision, the contrarian perspective asserts that empowering individuals and respecting their autonomy is essential for cultivating a vibrant and diverse society. It emphasizes the value of individual contributions and recognizes the potential for innovation, creativity, and progress that emerges when individuals are free to express their unique perspectives and ideas.
Moreover, the contrarian viewpoint emphasizes the importance of active citizen participation in shaping the direction and policies of society. It encourages a democratic and participatory framework where individuals have the opportunity to engage in decision-making processes, hold their leaders accountable, and contribute to the collective well-being.
By challenging Gentile’s prioritization of the state over individual autonomy, the contrarian perspective seeks to promote a more balanced and inclusive approach to governance. It advocates for a society that not only protects individual rights and freedoms but also values and encourages active participation, diversity, and the flourishing of individual potential.
The Ends Justify the Means: Machiavelli’s Influence on Fascist Leadership
The concept that “the ends justify the means” is often associated with Machiavelli’s political philosophy. It suggests that achieving desired outcomes or goals is of primary importance, and the methods used to achieve them can be justified, even if they involve unethical or morally questionable actions.
Critics argue that this perspective can be interpreted as justifying any action, regardless of its ethical implications. They express concerns that an uncritical embrace of this principle can lead to the disregard for moral principles, the erosion of ethical standards, and the justification of unethical behaviour.
It is important to note, however, that Machiavelli’s political thought is multifaceted and has been subject to various interpretations. Machiavelli’s work, particularly “The Prince,” is often studied for its analysis of political power and the strategies that leaders may employ to obtain and maintain it. While Machiavelli does discuss the use of force, deception, and manipulation, it is crucial to consider the historical context in which he was writing, which was characterized by political instability and Machiavelli’s desire to offer practical advice to rulers.
Moreover, it is essential to recognize that Machiavelli’s ideas do not constitute a comprehensive ethical or moral framework. His focus is primarily on the practical aspects of political power and leadership rather than providing a moral guide for human conduct.
Critics who challenge the idea that the ends justify the means often emphasize the importance of ethical considerations, the protection of human rights, and the adherence to moral principles. They argue that leaders should be held accountable for their actions and that the pursuit of desirable outcomes should not come at the expense of basic ethical standards.
Prioritizing Ethical Decision-Making: A Contrarian View of Machiavelli’s Ideas
The contrarian perspective challenges the foundational assumptions and beliefs that underpin fascist thought. It questions the notion that the state is the ultimate good and emphasizes the importance of individual liberty and autonomy. This viewpoint rejects the idea that the end justifies the means and prioritizes ethical decision-making and moral integrity.
Contrarians argue that the elevation of the state above all else can lead to the erosion of individual rights and freedoms, as well as the potential for authoritarianism and oppressive governance. They emphasize the value of individual autonomy and the right to self-determination, promoting a society that respects and protects the rights of its citizens.
Furthermore, the contrarian viewpoint challenges the idea that any action can be justified if it leads to a desired outcome. It emphasizes the ethical dimension of decision-making, asserting that the means employed to achieve an end are just as important as the end itself. Ethical considerations, such as fairness, justice, and respect for human rights, should guide individual and collective actions.
By adopting a contrarian perspective, one can critically examine the assumptions and beliefs that underpin fascist thought. This approach encourages a reevaluation of the values and principles that shape society, challenging the potential dangers of authoritarianism and advocating for a more ethical and inclusive approach to governance. It affirms the importance of individual rights, freedoms, and ethical decision-making as essential elements of a just and equitable society.
Developing a Nuanced and Critical Understanding of Mass Formation Psychology in Fascism
Developing a nuanced and critical understanding of mass formation psychology in Fascism requires questioning and challenging the ideas put forth by thinkers like Nietzsche, Gentile, and Machiavelli. A contrarian perspective allows for a comprehensive analysis that goes beyond accepting these ideas at face value, enabling a deeper understanding of the factors contributing to the emergence and appeal of fascist ideologies.
By adopting a contrarian approach, one can critically examine the assumptions, values, and implications of these ideas. This involves questioning Nietzsche’s “will to power” and its potential to justify oppression and violence, as well as challenging Gentile’s emphasis on the primacy of the state and the subordination of individual freedoms. It also entails interrogating Machiavelli’s notion that the ends justify the means and exploring the ethical implications of such a perspective.
Through this critical examination, a more comprehensive understanding of the psychological, social, and political factors that contributed to the rise of Fascism can be developed. It allows for a deeper exploration of the historical and socio-cultural context in which these ideologies emerged, as well as the underlying motivations and fears that drive individuals towards such beliefs.
Furthermore, a contrarian perspective emphasizes the importance of prioritizing individual liberties, ethical decision-making, and moral integrity in society. It challenges authoritarian tendencies, promotes the protection of human rights, and encourages the active participation of individuals in shaping the direction of their communities and organisations.
By critically engaging with the ideas of Nietzsche, Gentile, and Machiavelli and incorporating a contrarian perspective, we can develop a more nuanced and critical understanding of mass formation psychology in Fascism. This understanding can serve as a foundation for promoting individual liberties, ethical decision-making, and moral integrity to create a more just and inclusive society.
FAQs – Mass Formation Psychology Meaning
1. What is mass formation psychology?
Mass formation psychology studies examine how collective ideologies and group dynamics can shape individual behaviour and beliefs. It has broader implications for understanding how group dynamics influence people in various contexts.
2. What is a contrarian perspective?
A contrarian perspective questions and challenges the assumptions and beliefs that underpin the study of mass formation psychology and develops a more nuanced and critical understanding of the factors that underlie collective behaviour.
3. What is Nietzsche’s influence on fascist thought?
Nietzsche believed that Fascism was a product of the “will to power,” which drives human behaviour. However, a contrarian perspective challenges this view by highlighting that such an approach emphasizes the domination of the strong over the weak and can be seen as a justification for oppression and violence.
4. What is Gentile’s vision for a fascist society?
Gentile believed that the individual should submit to the will of the state to achieve a higher collective purpose. However, a contrarian approach questions Gentile’s notion of the importance of the state by pointing out that it prioritizes authoritarianism and the suppression of individual freedoms.
5. What is Machiavelli’s influence on fascist leadership?
Machiavelli’s idea that the ends justify the means can be seen as justifying any action, no matter how unethical.
6. What is the value of a contrarian perspective?
By adopting a contrarian perspective, one can interrogate the assumptions and beliefs that underpin the mass formation psychology of Fascism. This approach entails challenging the notion that the state is the ultimate good and affirming the importance of individual liberty and autonomy. It also involves rejecting the idea that the end justifies the means and prioritizing ethical decision-making and moral integrity.
7. How can we develop a nuanced and critical understanding of mass formation psychology in Fascism?
While the ideas of Nietzsche, Gentile, and Machiavelli have contributed to our understanding of the mass formation psychology of Fascism, a contrarian perspective allows us to question and challenge these ideas. By doing so, we can develop a more comprehensive and critical understanding of the factors contributing to this political ideology and work towards creating a society prioritising individual liberties, ethical decision-making, and moral integrity.
References
- Adorno, T. W., Frenkel-Brunswik, E., Levinson, D. J., & Sanford, R. N. (1950). The authoritarian personality. Harper & Brothers.
- Festinger, L., Riecken, H. W., & Schachter, S. (1956). When prophecy fails: A social and psychological study of a modern group that predicted the world’s destruction. Harper & Row.
- Janis, I. L. (1972). Victims of groupthink: A psychological study of foreign-policy decisions and fiascoes. Houghton Mifflin.
- Kershaw, I. (1999). Hitler: 1889-1936 Hubris. W. W. Norton & Company.
- Fromm, E. (1941). Escape from Freedom. Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
- Milgram, S. (1963). Behavioural study of obedience. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 67(4), 371-378.
- Arendt, H. (1951). The origins of totalitarianism. Harcourt Brace Jovanovich.
- Lipset, S. M., & Raab, E. (1978). The politics of unreason: Right-wing extremism in America, 1790-1970. University of Chicago Press.
Other Articles of Interest

Inflation News: Real Inflation Set to Surge

Resource Wars: Navigating a Shifting Global Landscape

Crisis Investing: Turning Market Crashes into Opportunities

Yuan Vs Yen: Yuan On course to Challenge Yen

ASAN Stock Price Trends: Poised for Takeoff or Set to Decline

Ultimate Oscillator: The Volatility Indicator

Navigating Success: Top Stocks of 2016
Is The Stock Market Crashing: Separating Signal from Noise

Greenspan Put: Why the Maestro has it Wrong?

Financial Insights: Cutting Through the Noise

Strategic Precision: Navigating with RSI MACD Mastery

Herd Mentality Psychology: Predicted crude oil bottom

New American Economy: Unreal Recovery, Debt Financing

Federal Reserve Bank Definition: Unveiling Deception and Fraud

What In God’s Name is Fluorescent Sand
Freedom from Religion: An Observer’s Perspective



