Define Fiat Money In Economics: Unlocking the Currency Conundrum
Updated Dec 24, 2024
The Truth About Fiat Money: Empty Promises and Potential Risks for Emerging Markets
When someone asks for a definition of fiat money, it can be explained simply as a currency with no backing other than false assurances or promises from a country to honour its debts. The risk for emerging markets, which heavily depend on short-term foreign capital, is that they might inadvertently drive it away and trigger a resurgence of inflation by excessively injecting newly created money into the system.
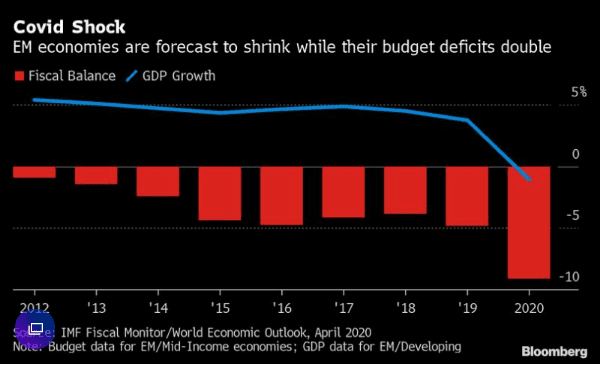
Emerging Economies Grapple with Mounting Outflows and Debt Pressures
In the current year, developing economies have faced significant capital outflows, exceeding those seen during the 2008 financial crisis. Currencies like Brazil’s real and Mexico’s peso have depreciated by over 20%, posing challenges for governments and businesses with dollar-denominated debt. The concern is that these countries may trigger a financial meltdown as they grapple with existing economic downturns. Rising COVID-19 cases and deepening recessions further complicate matters, potentially leading emerging markets to deviate from strict fiscal measures.
However, monetizing budget deficits could result in currency depreciation and worsen the crisis due to their reliance on external and foreign-currency financing. Experts in the field anticipate the possibility of many emerging markets abandoning fiscal constraints. https://yhoo.it/3bURiwM
The rest of the world cannot duplicate America’s deadly ability to create money out of thin air with almost no consequence. Before you start to say, look at how Gold is acting; if one looks at it closely, it has yet to test its old highs. In the interim, the money supply has almost tripled since it topped in 2011. We are hard-money fans, not gold bugs or hard-money fools. The masses have been conned, so the idea that Gold will soar to the moon is plain rubbish. It will trend higher but won’t outpace AI stocks and other sectors.
The Rise of Automation: Deflation and Job Elimination in the Post-Pandemic Era
A significant factor to consider will be deflation, as companies increasingly substitute humans with machines. The impact of the coronavirus pandemic has accelerated the testing of various new technologies, which, once finalized, will permanently eliminate numerous jobs.
The Dark Side of Monetary Policy: Consequences of the Fed’s Money Printing
The Federal Reserve has employed a clever strategy, flooding the markets with money and causing significant damage to various sectors through decreased demand. Influenced players have skillfully used fear, benefiting those who are shrewd and perceptive. However, it’s essential to recognize that not everyone can be a winner in life and investing.
There is a possibility that the Euro may not only reach parity with the dollar but even fall below it, but that is a topic for another discussion. It’s crucial to understand that this abundance of free money comes at a cost: personal freedom. When the printing press goes unchecked, it can lead to the emergence of oppressive forces akin to the Gestapo. Consequently, the United States and other highly regarded retirement destinations may continue to decline in their rankings. Fiat money and freedom are not compatible partners.
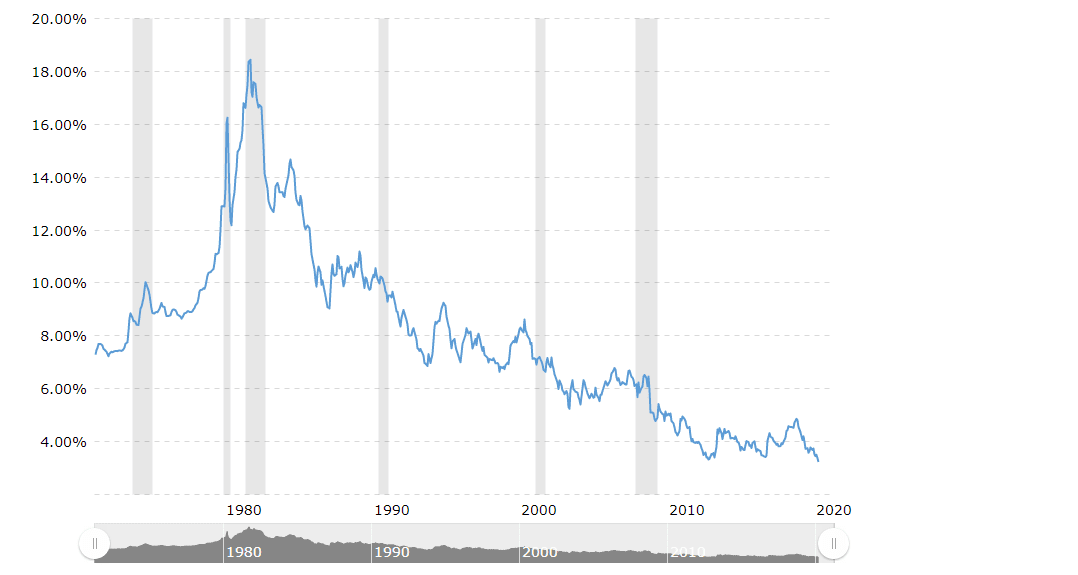
The Upward Trend of Housing Prices and the Role of Ultra-Low-Interest Rates
Paraphrased: This chart provides insight into the long-term upward trend of housing prices, driven by ultra-low interest rates that contribute to the formation of bubbles. Another perspective on defining fiat money is that it is a tool that has played a crucial role in fueling every bubble since the abandonment of the gold standard.
It is the primary reason behind the widening wealth gap, where the rich continue to prosper while the majority experience a decline in financial well-being.
Define Fiat Money In economics conclusion.
In conclusion, the truth about fiat money reveals the inherent risks and empty promises associated with its use, particularly for emerging markets. These economies face the challenge of capital outflows, mounting debt pressures, and the potential for currency devaluation. The COVID-19 pandemic has further exacerbated their economic downturns, leading to a temptation to deviate from fiscal constraints and monetize budgetary deficits. However, this approach can trigger a severe crisis due to their reliance on external financing and foreign currencies.
The ability of certain countries, like the United States, to create money out of thin air without immediate consequences is not easily replicable worldwide. While some argue that gold will soar in value, the reality is that its performance has yet to surpass previous highs despite the significant increase in the money supply. Furthermore, the rise of automation and job elimination in the post-pandemic era presents challenges, including potential deflationary pressures.
The dark side of monetary policy
As the Federal Reserve has witnessed, money printing has caused significant damage to various sectors by decreasing demand and distorting markets. While some individuals have profited from this strategy, it is essential to recognize that not everyone can be a winner in life and investing. Moreover, the unchecked expansion of the money supply can lead to losing personal freedom and the emergence of oppressive forces.
Ultra-low interest rates have contributed to the upward trend of housing prices and the formation of asset bubbles. This trend, coupled with the widening wealth gap, highlights the role of fiat money in exacerbating economic disparities.
In summary, using fiat money presents significant challenges and potential risks for emerging markets, impacts personal freedom, and contributes to economic distortions. Understanding these implications is crucial in navigating the complexities of the modern financial system and its dependence on fiat currencies.
Food for thought
According to Mass Psychology, the true purpose of Fiat is to exert control over the masses and prevent them from escaping the 9-5 routine cycle. This is achieved by deliberately devaluing the currency, creating an illusion of stability when things are not okay. Inflation, often called a silent killer tax, erodes the value of money over time. One potential solution is to adopt a contrarian perspective and invest in assets that have the potential to outpace currency devaluation. Such assets include the stock market, real estate, and precious metals.
Other Articles of Interest
Deflation Economics: The Art of Twisting Data
BTC vs Gold: The Clear Winner Is …
Russell 2000: Great Buy Signal In the making
Strong Buy Stocks: Focus on The Trend & Not the Fear Factor
Dow Jones Industrial Average Index Set To Defy Naysayers
Smart Money Acting Like Dumb Money
Market Crash 2020 Or Is This A Manufactured Crisis?













