
What Is Mob Psychology? Why Groups Think, Panic, and Crash Together
Fear not what you know; fear what you know not. – Sol Palha
April 12, 2025
Introduction
Mob psychology, or market psychology, delves into how the collective mind influences individual behavior, especially in financial markets. Drawing on the insights of thinkers like Sigmund Freud, Gustave Le Bon, and Wilfred Trotter, this field uncovers the powerful forces that drive group dynamics. Freud examined the subconscious influences, Le Bon defined the nature of crowd behavior, and Trotter introduced the “herd instinct” concept, explaining how group pressures often lead to collective action.
At its core, mob psychology focuses on the emotional extremes—fear, greed, and excitement—that sweep through markets, pushing them to irrational highs and lows. Investors who fail to recognize these psychological currents risk being swept up in the herd mentality. Contrarians, on the other hand, aim to exploit these extremes, making calculated moves when irrational impulses drive the crowd.
Historical events, like the 1929 crash or the 2008 financial crisis, are stark reminders of how powerful mob psychology can be. These crises show that understanding the psychological underpinnings of crowd behavior is crucial for navigating market turbulence. Recognizing these patterns allows investors to sidestep the dangers of herd mentality, using insight to make informed, contrarian decisions in volatile markets.
In essence, mob psychology is a critical lens for understanding market behavior, offering valuable insights for investors who seek to thrive amid emotional chaos.
Learning from History: A Guide to Market Sentiment Analysis
Market sentiment analysis provides investors with a framework for understanding the market’s collective mood. This approach, rooted in mass psychology, allows investors to anticipate market movements by recognizing the emotional undercurrents driving decisions. Successful contrarians have harnessed this knowledge throughout history, often profiting by going against the crowd at pivotal moments.
Expert Insights and Historical Examples:
- Baron Rothschild: Known for his famous advice, “The time to buy is when there’s blood in the streets,” Rothschild capitalized on market fear, such as during the panic after the Battle of Waterloo. While others sold in fear, he bought undervalued assets and amassed wealth.
- John Templeton: During the early days of World War II, Templeton bought shares of European companies trading for less than $1 per share, capitalizing on widespread fear. His investments paid off handsomely when the market rebounded post-war.
- Warren Buffett: Buffett’s contrarian approach is best illustrated during the 2008 financial crisis. While others were selling in panic, he seized the opportunity to invest in undervalued companies like Goldman Sachs and General Electric, securing immense returns when the market recovered.
Mass Psychology from Past to Present:
History shows that emotions, not rational analysis, often guide the masses in financial markets, creating opportunities for those who understand crowd psychology. Contrarians recognize these emotional extremes and capitalize on them:
- Panic Buying Opportunities: Market crashes, such as the Great Depression, Dot-com Bubble, and 2008 Crisis, demonstrate how mass panic selling can present buying opportunities for undervalued, high-quality companies.
- Euphoria Selling Signals: Conversely, the market becomes overvalued during euphoric periods like the Roaring Twenties or the pre-2000 Dot-com boom. Savvy investors recognize these signs of excess and act by selling into the rally.
By applying sentiment analysis and understanding the psychology of crowds, investors can navigate market cycles, buying when fear grips the market and selling when the herd is caught in the grip of irrational exuberance. By studying history and contrarian strategies, one can learn to profit from the emotional extremes that drive market behavior.
The Role of Crowd Psychology in Driving Market Prices
Market psychology plays a critical role in the stock market, where the emotions and actions of a large group of people can drive prices. Crowd psychology, the study of mass mindset and behaviour, can explain why investors sometimes act irrationally and why market prices can experience dramatic swings.
The comic strip and accompanying article provide a visual and clear illustration of the principle of crowd psychology in action in the stock market. By showing the contrast between the emotions of fear and panic on one side and optimism and excitement on the other, they highlight the idea that the feelings of a large group of people can drive market prices. The strip also distinguishes between crowd psychology and fashion contrarianism, pointing out that the latter is based on appearance or trend-following rather than a deep understanding of market forces.
The illustration reminds us that emotions influence market prices, and we should approach investing with a long-term, well-informed perspective rather than simply following the crowd or jumping on the latest trend.
The Famous Investment Strategy of “Buy the Panic and Sell the Joy
The adage “buy the panic and sell the joy” encapsulates a contrarian investment philosophy that capitalizes on the emotional extremes of the stock market. It’s predicated on the idea that investor sentiment often swings between fear and greed, which can lead to market overreactions. During widespread panic, assets may become undervalued as investors flee the market, presenting buying opportunities for the astute investor. Conversely, when the market is buoyant, and investors are overly optimistic, asset prices may inflate, signalling a time to sell.
The Risks of a Crowd Psychology-based Investment Strategy
While this strategy is grounded in the principles of crowd psychology, it carries inherent risks. The stock market is influenced by a myriad of factors beyond just investor sentiment, including macroeconomic indicators, geopolitical events, interest rate changes, and corporate earnings reports. A strategy based solely on the emotional state of the market can lead to misjudgment and financial loss if these other factors are not considered.
To employ this strategy effectively, an investor must understand market psychology by comprehensively analysing economic conditions and individual company performance. This balanced approach can help investors avoid emotional decision-making and maintain a focus on long-term financial objectives.
Practical Application of Market Psychology
The practical application of this strategy requires discipline and a contrarian mindset. Historical market trends show that the masses often get it wrong at critical junctures:
– During market crashes, fear can lead to a sell-off, but for discerning investors, this can be the optimal time to acquire quality stocks at a discount.
– In times of market euphoria, when investors are piling into the market, it may be prudent to take profits as valuations stretch beyond reasonable levels.
The key is maintaining a level-headed approach, using sentiment as a gauge rather than a directive. By understanding the psychological drivers of market movements and combining this with solid fundamental analysis, investors can navigate the market’s highs and lows more effectively. The strategy of “buy the panic and sell the joy” is not about timing the market perfectly but rather about recognizing and acting on the opportunities that arise when the emotional pendulum of the market swings too far in either direction.
Market Psychology clearly states that one should only abandon ship when the masses are joyful.
Market Psychology and Crowd Dynamics in the Stock Market
Understanding market psychology and the dynamics of crowd behavior is essential for investors navigating today’s volatile financial landscape. While technical analysis can pinpoint market turning points, crowd psychology’s unseen force—particularly herd mentality and the bandwagon effect—often dictates market outcomes. Investors who incorporate mass psychology into their strategy, taking a contrarian approach, are better positioned to avoid the common pitfalls of following the crowd and making decisions based on short-term emotional impulses.
Contrarian Insights from Investing Legends:
- Charlie Munger: Warren Buffett’s right-hand man, Charlie Munger, has long emphasized the power of thinking differently from the crowd. Munger’s advocacy for “inversion”—the practice of thinking about what others are avoiding or fearing—captures his contrarian philosophy. He suggests that when the market is in panic mode, it may very well be the optimal time to buy.
- Peter Lynch: As the manager of the Fidelity Magellan Fund, Peter Lynch found success by focusing on what he knew and identifying undervalued opportunities in the market. His success came from tuning out the crowd, focusing on a company’s intrinsic value, and making decisions based on thorough research rather than popular sentiment.
- John Bogle: Known as the father of index fund investing, John Bogle championed long-term investment strategies that minimize costs. He understood that emotional investing often leads to rash decisions, higher transaction costs, and lower returns. His philosophy—rooted in the idea of staying the course despite short-term market noise—also stands as a form of contrarian investing.
Applying Investment Principles to Life:
The principles behind contrarian investing can also be applied beyond financial markets. Just as in investing, life requires balancing conformity with forging one’s own path. Being skeptical of popular opinion, focusing on long-term goals, and trusting in your research and intuition are essential for personal growth and sound decision-making. Just as an investor might look beyond the immediate market mood, so too must individuals make choices that reflect their values and long-term vision.
The Role of a Trading Journal:
A trading journal is more than just a record of trades; it’s a vital tool for reflecting on the decisions made, both good and bad. It helps identify patterns, refine strategies, and develop the mental discipline required for future success. In the ever-changing world of market psychology, a trading journal offers insight into how emotions and crowd dynamics influenced past actions, helping investors learn from both mistakes and triumphs.
Okay, now let’s shift to a historical perspective. Exploring historical perspectives empowers individuals to learn from the past, avoid mistakes and make informed decisions for a secure and prosperous
The Masses Are Nervous
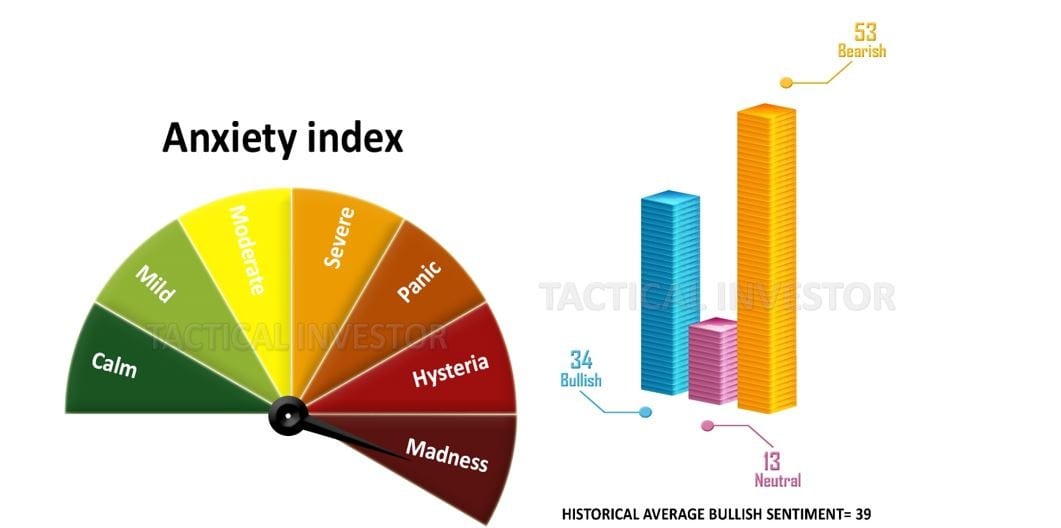
The crowd is not in a good mood. They panic and make decisions based on their emotions. This often leads to selling and missing out on opportunities in the long run. When things settle down, the market usually bounces back, but people tend to repeat their mistakes and make the same emotional decisions again.
Once again, they (the crowd)will promise not to repeat their mistakes, but like crack heads they will do exactly the same thing and precisely the worst moment, ensuring they remain in the dog house forever. Sol Palha
Conclusion:
Ultimately, the stock market is driven not just by technical indicators but by the psychology of the masses. Those who master both technical analysis and an understanding of crowd behavior are better equipped to make informed decisions, avoiding the emotional pitfalls of herd mentality. By adopting a contrarian mindset, as illustrated by investing legends like Munger, Lynch, and Bogle, investors can achieve financial success and personal growth. Through discipline, emotional detachment, and long-term vision, one can navigate the market’s unpredictable ebb and flow and secure enduring prosperity.
Other Articles of Interest













