Unravelling the student loan debt crisis: Navigating the Tides of Educational Finance
Updated Nov 25, 2023
In the rhythmic pulse of society, a resounding heartbeat echoes through the halls of academia—the relentless rhythm of student loan debt. The student loan debt crisis, a term whispered in hushed tones, has become a racket impossible to ignore. As students embark on the noble quest for knowledge, they find themselves entangled in the intricate web of financial obligations, raising a pivotal question: Are we on the precipice of an educational finance revolution?
Like a gathering storm, the crisis has far-reaching consequences, reshaping the landscape of aspirations and dreams. It is a narrative etched in the struggle of countless students, the weight of loan burdens stifling their pursuit of intellectual growth. The burgeoning debt crisis is not merely a financial woe but a societal challenge, threatening to undermine the foundations of equitable educational access.
The spotlight turns to the mechanisms and structures perpetuating this crisis in this unfolding saga. The intricate dance between educational institutions, financial systems, and government policies is scrutinised, revealing a tapestry woven with complexities and disparities. The need for a comprehensive examination of this intricate web becomes apparent as the crisis extends its tendrils into the future, shaping the destinies of future generations.
As the clock ticks on this educational finance conundrum, the call for reform echoes louder. Can we envision a future where the pursuit of knowledge is liberated from the shackles of insurmountable debt? The answers lie not only in dissecting the crisis but also in crafting innovative solutions that transcend traditional paradigms. The quest for a brighter educational future beckons, challenging us to navigate the tides of change and forge a new path toward accessible and equitable learning.
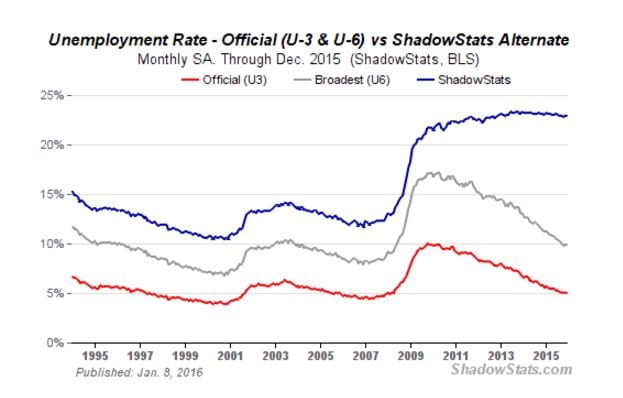
The chart below illustrates that unemployment is not 5%, as the BLS states, but almost 23%, as indicated by shadow stats.
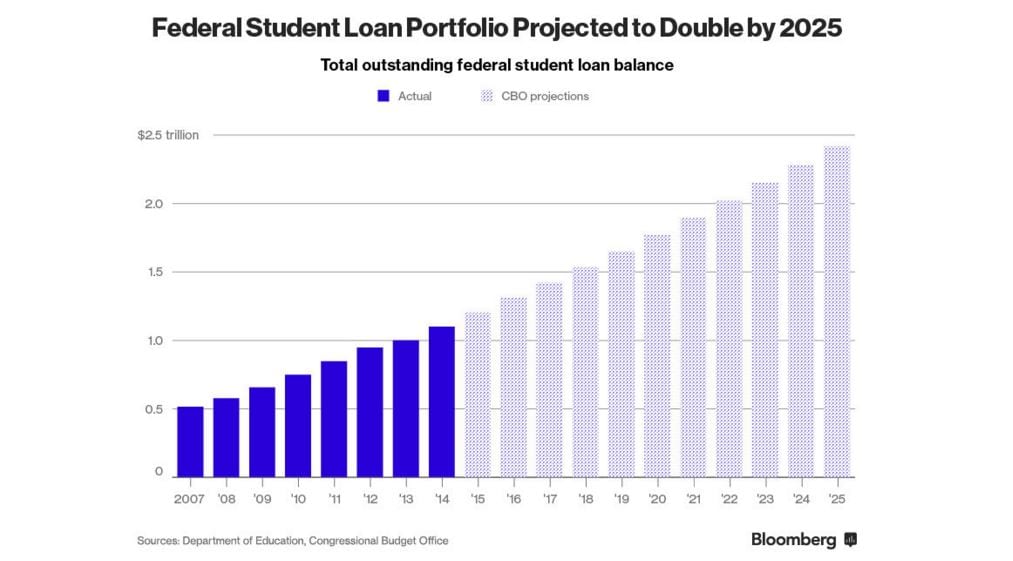
Student Loan Debt Crisis Due to Students Taking on Too Much Debt
Students are taking on too much debt with almost no hope of being able to pay it back. The student loan portfolio is set to almost double by 2025 to nearly $2.5 trillion by 2025. Already almost 12% of individuals are delinquent on their student loans, and the rate will only increase with time.
There are solutions to this problem, one of which is to live below your means and put this money into the stock market, but you need to know which companies to get into and when to get into them. Subscribe to our free newsletter to learn how to spot opportunities before the masses do and how to improve your odds of winning in the markets. Mass psychology states that opportunity is found in places the crowd cannot see or ignore. The trend is your friend; everything else is your foe.
Student Debt Crisis Overblown, and Due to Stupidity: Video
The Financial Landscape: Navigating Beyond the Crisis
The financial landscape of education is undergoing a metamorphosis, with the student loan debt crisis acting as a catalyst for change. As we navigate beyond the crisis, alternative models of educational finance come into focus. Countries worldwide are experimenting with tuition-free education, income-share agreements, and other innovative approaches.
Contrarianism, in this context, is not a denial of financial responsibility but an exploration of alternative avenues that align with the evolving needs of society. It invites us to consider models that shift the burden away from individual students, fostering a collective educational responsibility.
In the wake of the student loan debt crisis, the call for tuition-free education has gained momentum as an alternative model to the traditional fee-based system. Nations such as Germany and Sweden have embraced this approach, viewing education as a public good rather than a commodity. By eliminating tuition fees, these countries aim to ensure that financial constraints do not hinder access to education, thus cultivating a more equitable and inclusive educational landscape.
Income-share agreements (ISAs) emerged as a dynamic financial tool challenging the traditional loan system. Unlike conventional loans, ISAs tie the cost of education to a percentage of a graduate’s future income. This innovative approach aligns educational institutions’ interests with their students’ success. Institutions benefit if graduates thrive in their careers; if they face challenges, the financial burden is shared. ISAs create a symbiotic relationship that transforms education into a collaborative venture with shared risks and rewards.
Moreover, the growing emphasis on corporate responsibility has increased employer-sponsored education programs. Companies, recognizing the importance of a skilled workforce, are investing in the education of their employees. This alleviates the financial strain on individual students and ensures that the skills acquired are directly applicable in the workplace. By actively participating in educational finance, the corporate sector becomes a stakeholder in the continuous development of a knowledgeable and capable workforce.
The digital age has further transformed the financial landscape of education. Online learning platforms and open educational resources provide cost-effective alternatives to traditional classroom-based education. The accessibility offered by these digital tools allows a broader demographic to engage in learning, breaking down financial barriers and fostering a culture of continuous education.
As we navigate beyond the crisis, the financial metamorphosis of education invites us to reimagine the role of the collective in shouldering the responsibility of education. The evolution from individual financial burdens to shared responsibilities reflects a shift towards a more sustainable and inclusive educational model. In this dynamic landscape, financial innovation becomes a driving force, propelling education into a realm where knowledge is not only accessible but also a shared commitment to the advancement of society.
A Glimpse into the Future: Shaping a New Educational Paradigm
The contours of the future educational landscape are being etched by the currents of change brought about by the student loan debt crisis. As we gaze into the crystal ball of academia, a vision emerges—where education is liberated from the financial constraints that have long tethered it.
As a guiding philosophy, contrarianism propels us into this future, urging us to challenge preconceived notions and embrace innovative solutions. Once viewed as a harbinger of doom, the student loan debt crisis becomes a catalyst for transformation. This metamorphosis heralds an era where education is a right, not a privilege.
In this unfolding narrative, the concept of a tuition-free education gains prominence as a beacon of hope. Nations like Norway and Finland exemplify the possibility of this paradigm shift, where education is considered a fundamental right accessible to all. By dismantling financial barriers, these countries foster an environment where individuals can pursue knowledge without the looming spectre of debt, laying the groundwork for a more egalitarian educational paradigm.
The rise of income-share agreements (ISAs) further punctuates this vision of the future. As a departure from traditional loan systems, ISAs create a dynamic link between educational institutions and the success of their graduates. This symbiotic relationship aligns the incentives of both parties, transforming education into an investment with shared risks and rewards. The future of education could be one where institutions are not just providers of knowledge but active partners in the long-term success of their students.
Moreover, the collaborative efforts between the public and private sectors have become instrumental in shaping this new educational paradigm. The emergence of public-private educational partnerships, where governments and corporations work together to fund and facilitate learning initiatives, signals a departure from solely relying on individual finances. This collaborative approach ensures that the financial responsibility for education is distributed across a spectrum of stakeholders, lessening the burden on individual students.
The digital revolution continues to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of education. Online learning platforms, augmented reality, and artificial intelligence create a dynamic and interactive educational experience. This not only makes education more accessible but also reduces the costs associated with traditional brick-and-mortar institutions. The future might shift towards a more personalized and technology-driven educational landscape, providing learners with flexibility and affordability.
As we catch a glimpse of the future, the contours of a new educational paradigm come into focus. It is a paradigm where education is not merely a commodity but a shared responsibility, where financial barriers are dismantled, and innovative solutions propel academia into a realm of accessibility and equity. The currents of change set in motion by the student loan debt crisis become the transformative forces that shape a future where education is not a privilege reserved for a few but a right accessible to all.
Conclusion: Navigating the Seas of Change
In the symphony of societal evolution, the student loan debt crisis plays a defining chord. Its resonance echoes through the corridors of education, challenging us to redefine the essence of learning. As we navigate the seas of change, a contrarian spirit beckons us to question, innovate, and forge a new path—one where education is not a burden but a beacon guiding us toward a brighter, more equitable future.
In this contrarian narrative, the student loan debt crisis becomes not just a problem to be solved but a call to action—a call to reimagine education, to break free from the chains of convention, and to shape a future where the pursuit of knowledge is truly unbridled. The waves of change are upon us, and as we set sail into this uncharted territory, the contrarian approach becomes our compass, guiding us toward a horizon where education is a transformative force, unencumbered by the weight of debt.
Other related articles
The Long Game: Why Time in the Markets Beats Timing the Markets