Fed Data Paints Murky Picture?
Updated Dec 2022
If the economic recovery were truly genuine, interest rates would not have remained at such low levels for so long, and the Fed would not have needed to support the stock market. Instead, corporations have resorted to the illegal use of stock buybacks, focusing solely on artificially boosting EPS by buying back shares. This fraudulent scheme allows for large payoffs with little work, and with low interest rates, the incentive to borrow vast sums of money for these deceptive practices is stronger than ever. As a result, we should anticipate stock buybacks to reach unprecedented levels in the near future.
Unfortunately, the truth is that economic recovery is nothing but a bad joke, as illustrated by this one chart. The corporate world’s reliance on stock buybacks to inflate EPS clearly indicates that the economy is not as healthy as it appears on the surface.
While some data points like GDP figures and unemployment rates have improved since the depths of the pandemic, there are reasons to be sceptical about the strength and sustainability of the recovery. For instance, GDP is not accounting correctly for inflation, which means real economic growth is likely much weaker than the headline numbers suggest. Additionally, much of the drop in unemployment can be attributed to workers dropping out of the labour force altogether rather than finding jobs. As such, the recovery may not be as robust as the Fed claims, and low-interest rates may continue to prop up unsound conditions rather than enable healthy growth over the long term. A more balanced approach is needed to assess the actual state of the economy.
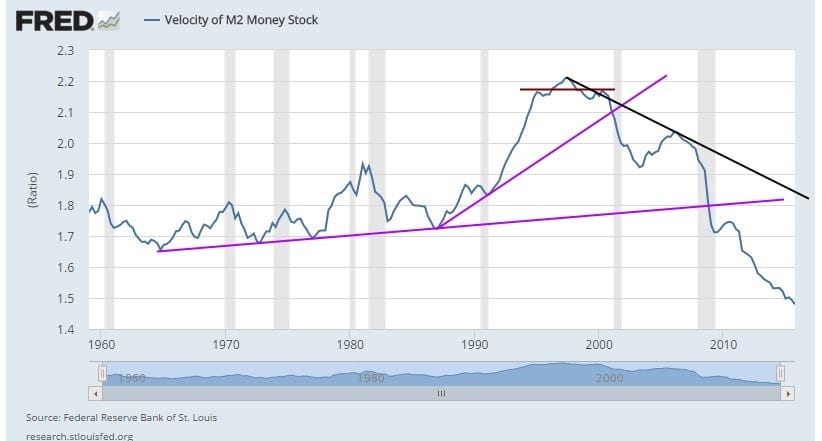
The chart shows this entire economic recovery is nothing but a hoax.
Fed Data and Economic Recovery
This chart is straightforward to understand. When the economy is booming, the velocity of money increases and vice versa; this chart topped out in 2000 with a double top formation. We did get a small pop-up when Greenspan flooded the markets with money to create the housing bubble, but it put us at a lower high. After that, it has been a downhill ride, which is why Gold prices have tanked. The money supply has increased, but the money is not moving. The masses do not have access to this money yet.
This is why we stated that if they really want to create a monstrous bubble, they need to put this money into the hands of the masses.
While specific metrics point to recovery, a closer look at the data paints a less rosy picture. The velocity of money, which measures how quickly dollars circulate through the economy, remains stubbornly low despite massive monetary stimulus. This suggests the recovery may be artificial rather than driven by sustainable, broad-based economic activity. Similarly, labour force participation remains depressed as many have stopped looking for work. Beyond headline figures, the economy’s underlying health and the recovery’s strength remain uncertain. Continued support from the Fed also risks inflating unsustainable bubbles down the road. More must be done to generate genuinely shared and inclusive growth that can restore velocity and full participation in the labour market. Otherwise, recovery may remain tepid, dependent on intervention, leaving many workers and communities behind.
Only the masses are foolish enough to take markets to levels you can only envision after smoking some illegal substance. This is why we are dead certain that the Fed will come out with another stimulus plan; this economic recovery is being held up by fiat money and nothing else.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the data paints a sobering picture of the so-called economic recovery. While specific indicators like GDP and unemployment rates may show signs of improvement, a deeper analysis reveals a different story. The prolonged period of low-interest rates and the Federal Reserve’s support for the stock market raise questions about the authenticity of this recovery.
The reliance on stock buybacks by corporations to artificially inflate earnings per share (EPS) indicates an economy that may not be as robust as it appears on the surface. This strategy, driven by low-interest rates, incentivizes large-scale borrowing for what can be viewed as deceptive practices. The expectation is that stock buybacks will continue to surge to unprecedented levels.
Furthermore, examining metrics like the velocity of money and labour force participation reveals a more troubling reality. The economy’s underlying health and the sustainability of the recovery remain uncertain. The velocity of money remains low, suggesting that the recovery may be artificial rather than driven by genuine economic activity. Labour force participation has not rebounded as expected, with many individuals ceasing to seek employment.
In essence, this economic recovery appears to be propped up by monetary policy measures, leading to concerns about its sustainability. To achieve a more robust and genuinely inclusive recovery, there is a need for a more balanced approach that addresses the underlying economic conditions and fosters broad-based growth. Otherwise, the recovery may remain fragile, reliant on intervention, and leave many individuals and communities struggling to benefit from it.
From Classics to Current: Other related stories: